Matthew Nguyen
@matt___nguyen
ID: 1692256330076098560
17-08-2023 19:25:55
10 Tweet
6 Followers
1 Following

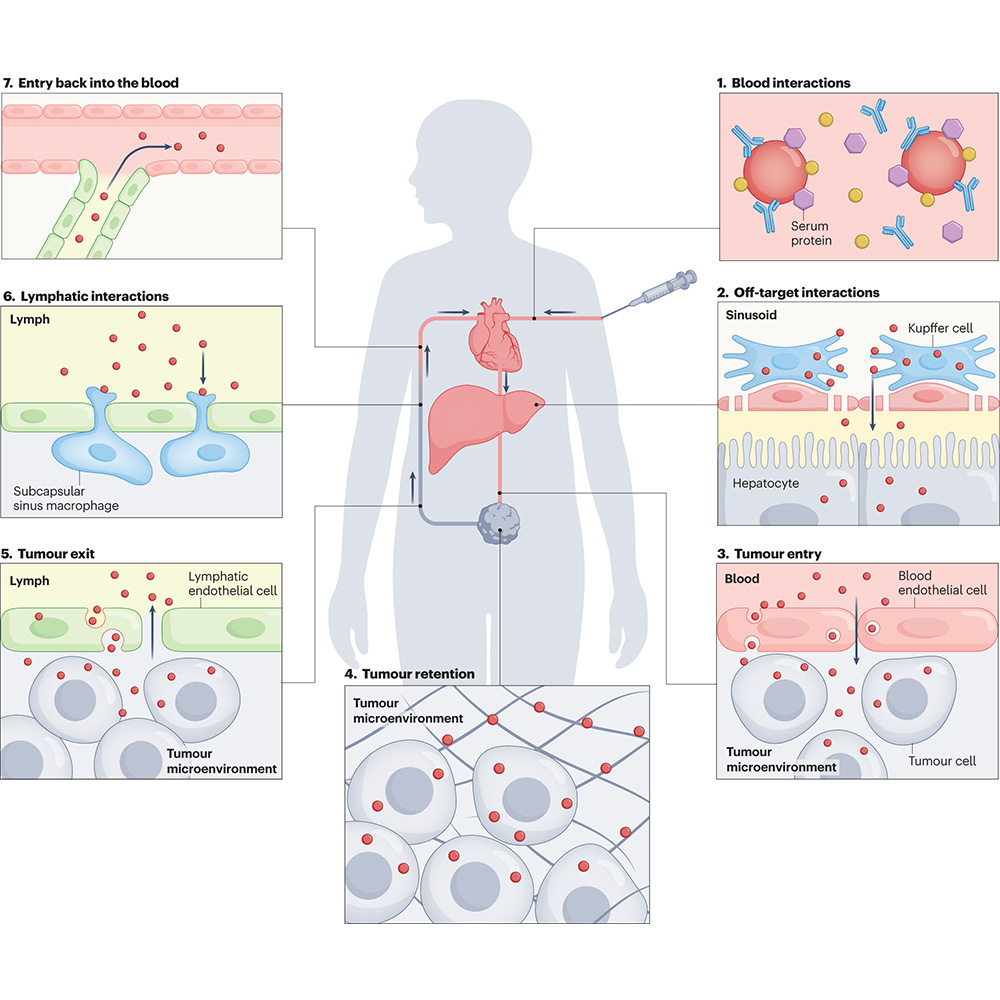
🚨🚨🚨🚨 Led by Matt, Our next blockbuster paper from The Chan Lab is out now in Nature Materials. We present the new mechanism of Active transport and retention and answered How nanoparticles exit from solid tumours | Nature Materials nature.com/articles/s4156…

The exit of nanoparticles from solid tumours The Chan Lab go.nature.com/3sgAAVB


A nanoparticle delivery paradigm in cancer – the EPR effect - has been challenged, shifting the focus to active delivery mechanisms. In their Review, Warren Chan et al explore passive vs active delivery and the impact on nanoparticle design The Chan Lab go.nature.com/3OBvP1s

The Chan Lab has made advances on mechanisms of cancer nanomedicine in the last 10 years. Led by Matthew Nguyen, our new review Nature Reviews Bioengineering takes a deep dive on EPR effect vs Active Transport & Retention principle and importantly challenges ahead. Link: nature.com/articles/s4422…



A Review in Nature Reviews Bioengineering discusses two contrasting nanoparticle delivery mechanisms, the enhanced permeability and retention effect and the active transport and retention principle, and their implications for the design of cancer nanomedicines. 🔒 go.nature.com/3IalYMj



This month it’s all about nanoparticle delivery mechanisms! Do not miss the Review by The Chan Lab on the mechanisms of nanoparticle delivery to solid tumours. Now free to access: go.nature.com/3OBvP1s

A Review in Nature Reviews Bioengineering discusses two contrasting nanoparticle delivery mechanisms, the enhanced permeability and retention effect and the active transport and retention principle, and their implications for the design of cancer nanomedicines. 🔒 go.nature.com/3IalYMj