Catherine Xu
@catherine_k_xu
@HFSP fellow in @GuckLab at @MPI_Light | alumna of @KnowlesLabCamb at @ChemCambridge
ID: 1515743229957840900
17-04-2022 17:25:40
21 Tweet
44 Takipçi
85 Takip Edilen



Thanks to everyone involved, in particular co first author Catherine Xu, for a great collaboration! KnowlesLab Cambridge KlenermanLab @MichaelsLabUCL @daniel_otzen, Jonathan Taylor, Aviad Levin, Steve Matthews, Sara Linse and Maria Andreasen Cambridge Chemistry Science Advances

Some amyloid fibrils fulfill functional roles whereas others are the cause of neurodegenerative diseases. Our new paper in Science Advances by Georg Meisl and Catherine Xu sheds light on why that might be: science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…




Check out our new PNAS paper pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38652742/ Using a method originally developed in astronomy, we determine the half lives of all proteins in a cells, in a single set of experiments. Congrats to Alex & everyone involved on a really cool paper! KnowlesLab Cambridge PNASNews


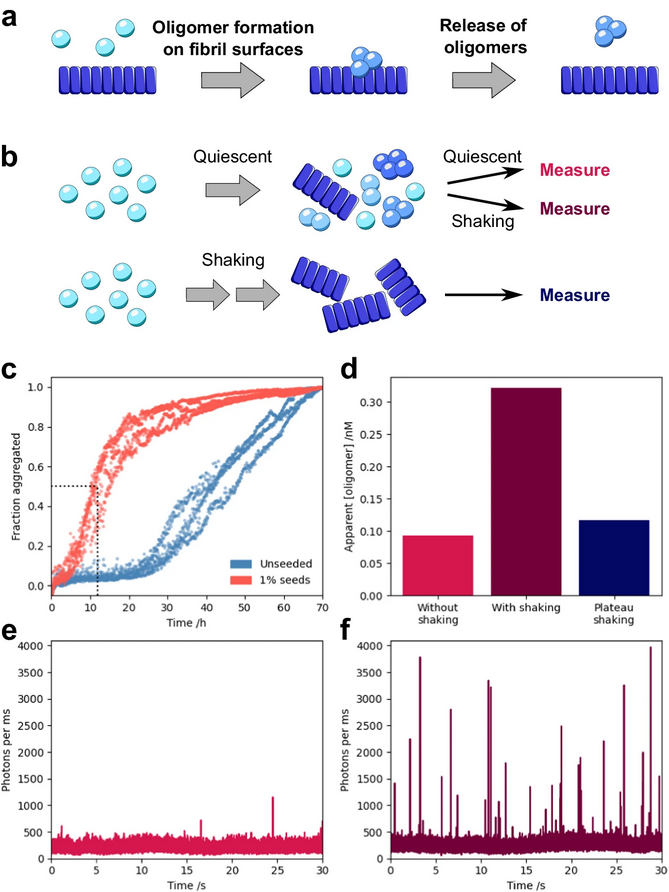
In many systems, toxic protein oligomers are produced by nucleation on existing fibrils, but how are they removed? We show that fibrils also effectively catalyse oligomer dissociation, with interesting implications for drug discovery in ACSChemNeurosci doi.org/10.1021/acsche…


Fundamental insights into the influence of sheer forces in amyloid formation - great work by Ewa Andrzejewska and Greta Šneiderienė led by Emil and others from the Linse lab is now out: pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pn…

So happy to see this out! Many thanks to all involved: Marcus Gutmann (not on X) Jana Bachir Salvador Paul Müller Kyoohyun Kim Martin Schicht (not on X) Serhii Aif 🇺🇦 Friedrich Paulsen Lorenz Meinel (not on X) GuckLab 🇺🇦

Nice to be a part of this collaboration studying the binding mechanism of synuclein oligomers with lipid membranes, that play a role in Parkinson's disease pathology. Well done Greta Šneiderienė Magda Czekalska Catherine Xu KnowlesLab Cambridge doi.org/10.1021/acsnan…

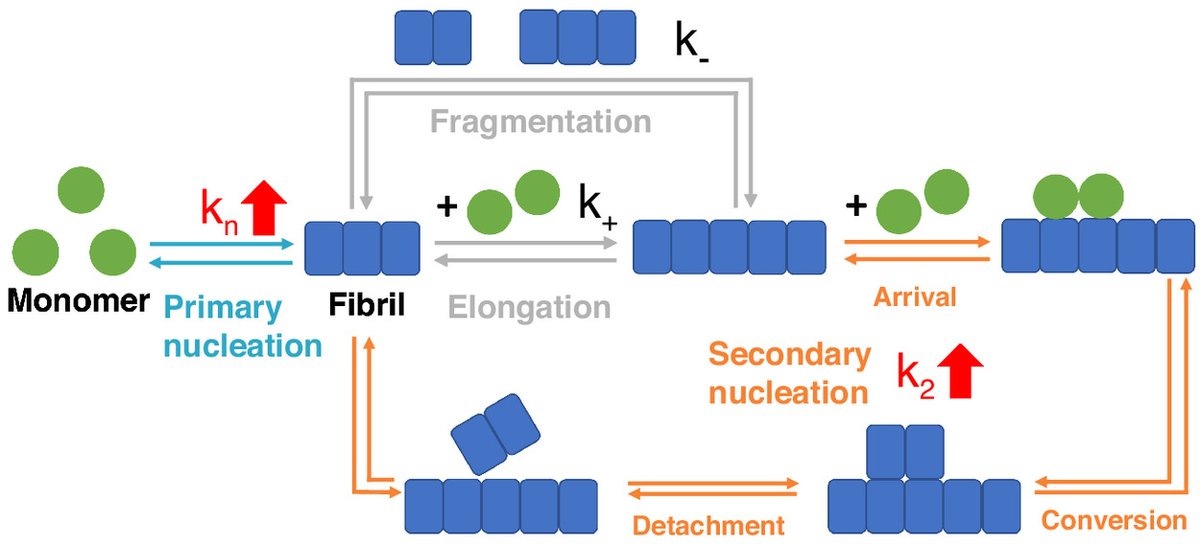
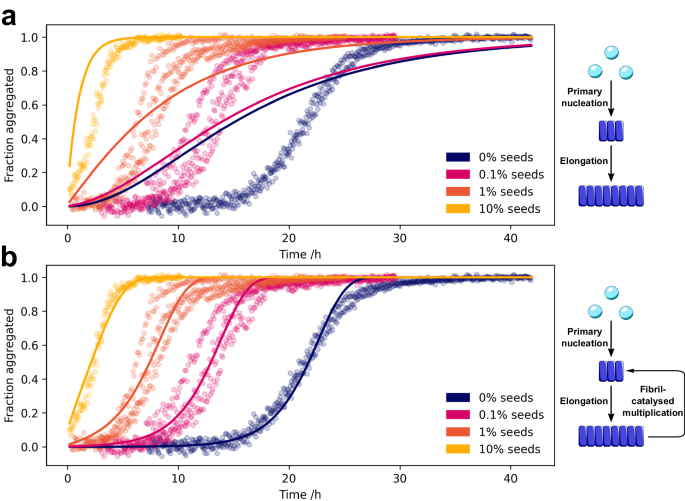
New paper from Catherine Xu KnowlesLab Cambridge & collaborators reports secondary nucleation as not only the key source of a-synuclein oligomers, "but also the main mechanism of aggregate formation"; The process can occur under neutral pH & ionic strength nature.com/articles/s4146…

Our latest paper by Catherine Xu - secondary nucleation is the source of both oligomers and fibrils in Parkinson's associated a-Synuclein aggregation. Fantastic collaboration with Linse lab SpillantiniLab and Vendruscolo Lab nature.com/articles/s4146…

Catherine Xu KnowlesLab Cambridge Cambridge Chemistry show that at physiological pH and in the absence of lipid membranes, α-synuclein aggregates form by secondary nucleation, and that this process is enhanced by agitation. nature.com/articles/s4146…

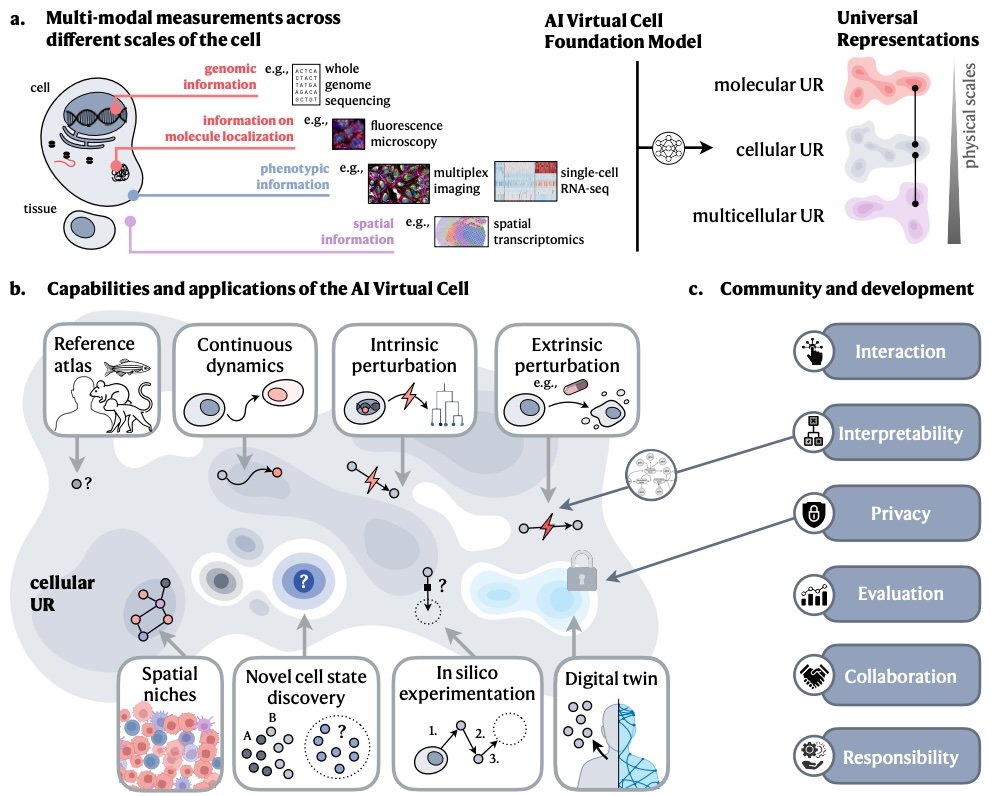
Check out our perspective article on AI-powered Virtual Cells. This is a result of an exciting collaboration with Stephen Quake Jure Leskovec Aviv Regev, Bougatsa Charlotte Bunne Yusuf Roohani @yanayrosen Chan Zuckerberg Initiative and extensive community discussions. arxiv.org/pdf/2409.11654