BerkeleyNLP
@berkeleynlp
We work on natural language processing, machine learning, linguistics, and deep learning.
ID: 1173334037777141760
http://nlp.cs.berkeley.edu/ 15-09-2019 20:33:38
109 Tweet
5,5K Followers
33 Following

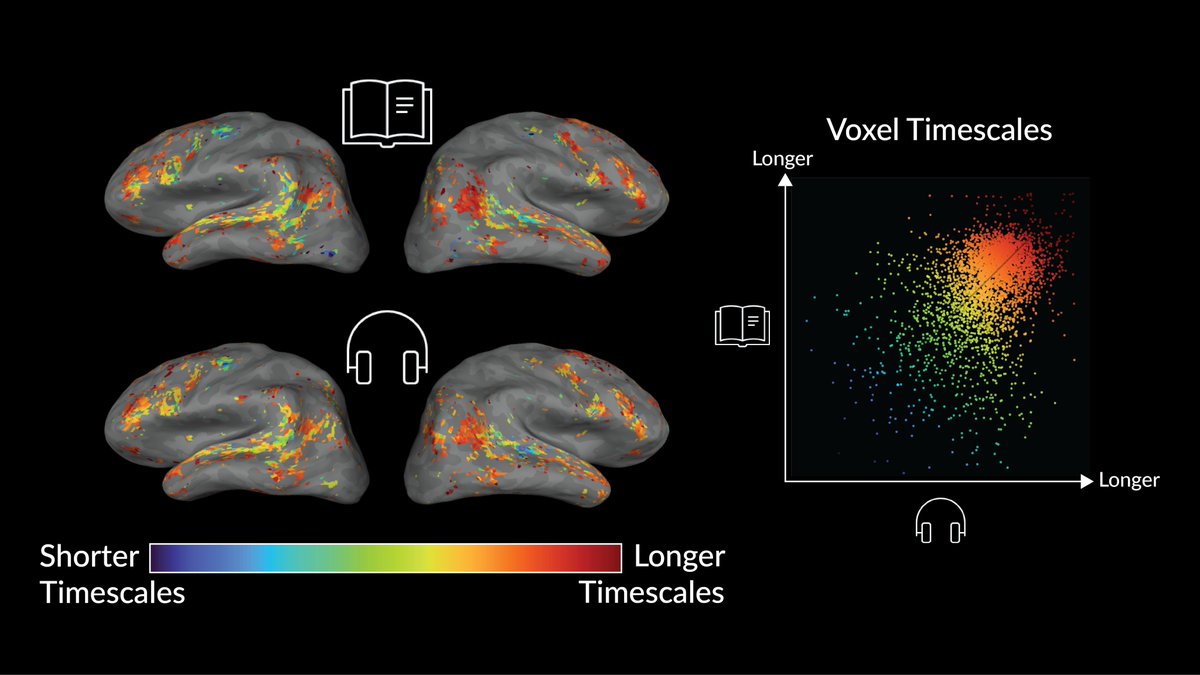
Do brain representations of language depend on whether the inputs are pixels or sounds? Our Communications Biology paper studies this question from the perspective of language timescales. We find that representations are highly similar between modalities! rdcu.be/dACh5 1/8



Excited to share some recent work! "Pose Priors from Language Models" We show how to use multimodal LMs to improve 3D human pose estimates in situations with physical contact. Joint work w/ Evonne Ng , Lea Müller , Dan Klein (BerkeleyNLP), Shiry Ginosar , trevordarrell










Cool new dataset for translation ambiguity in 9 language pairs (7 low-resource), and we found LLM-generated descriptions help weaker models resolve ambiguity! Josh Barua will be presenting this at the 2-3:30pm poster session today, come talk to us about multilinguality in LLMs!




Finished my dissertation!!! (scalable oversight,link below) Very fortunate to have Jacob Steinhardt and Dan Klein as my advisors! Words can't describe my gratitude, so I used a pic of Frieren w/ her advisor :) Thanks for developing my research mission, and teaching me magic



![Jiayi Pan (@jiayi_pirate) on Twitter photo New paper from @Berkeley_AI on Autonomous Evaluation and Refinement of Digital Agents!
We show that VLM/LLM-based evaluators can significantly improve the performance of agents for web browsing and device control, advancing sotas by 29% to 75%.
arxiv.org/abs/2404.06474 [🧵] New paper from @Berkeley_AI on Autonomous Evaluation and Refinement of Digital Agents!
We show that VLM/LLM-based evaluators can significantly improve the performance of agents for web browsing and device control, advancing sotas by 29% to 75%.
arxiv.org/abs/2404.06474 [🧵]](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/GK0M2S8bEAAduvw.jpg)