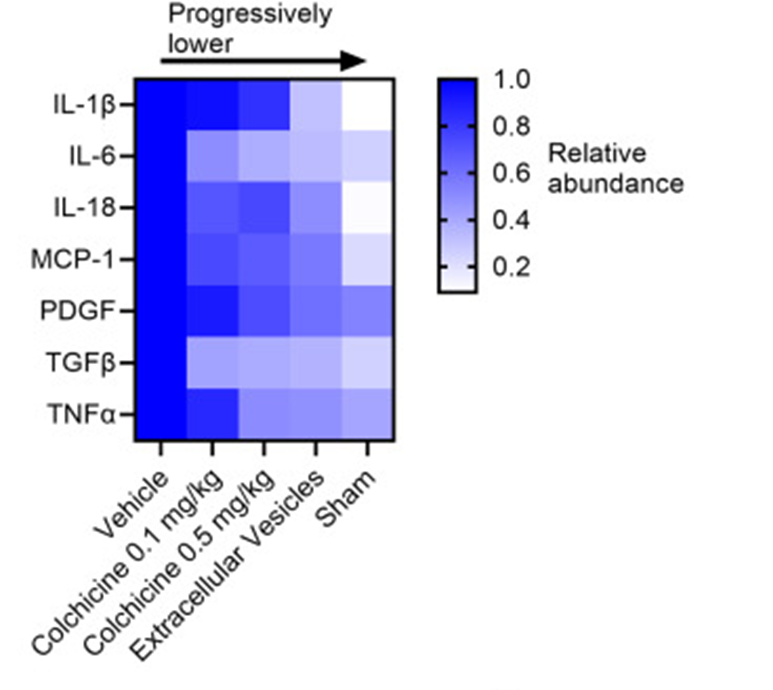
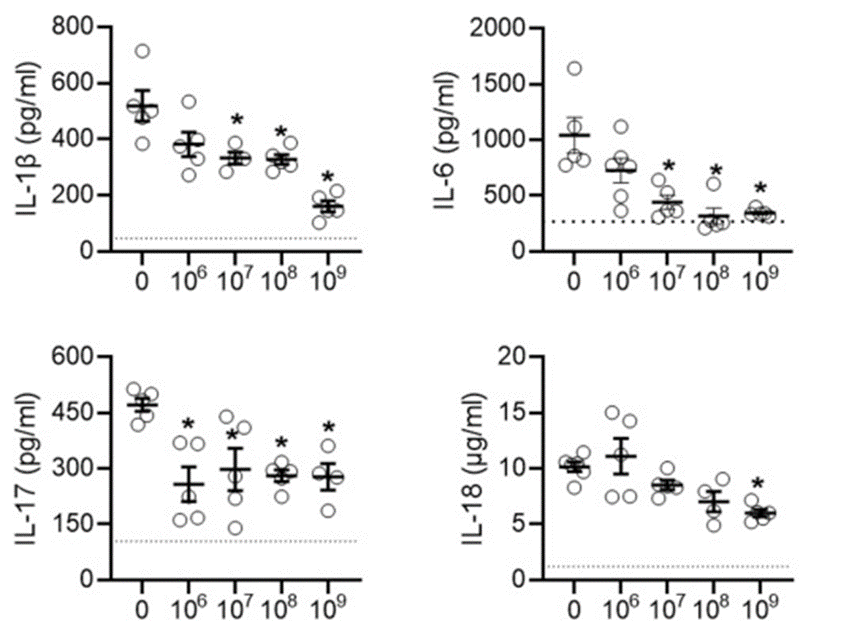
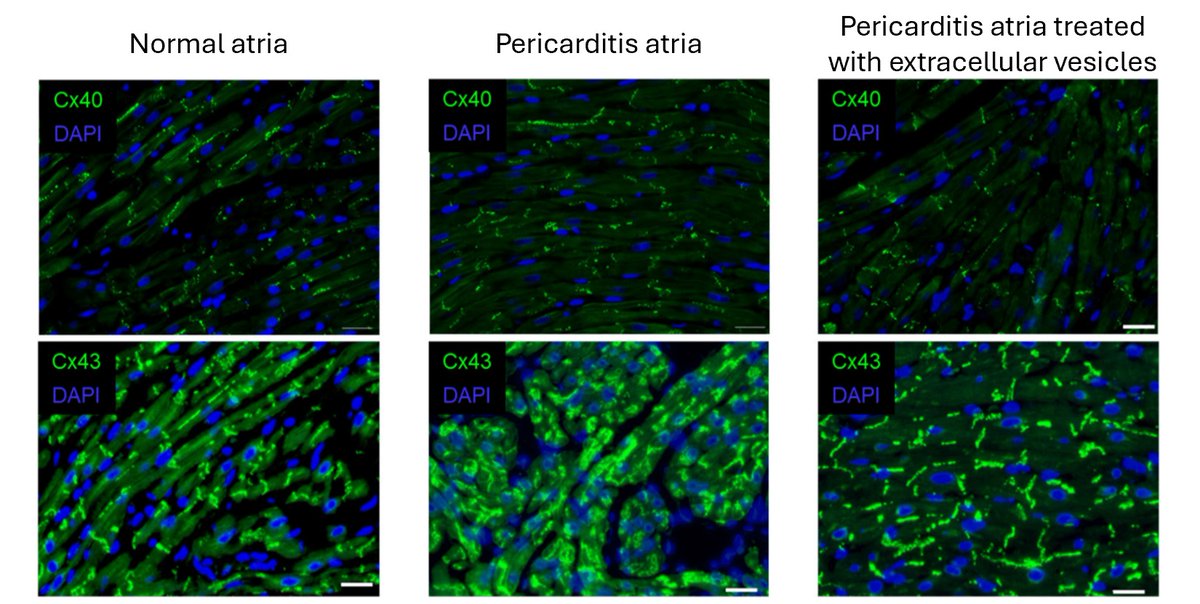
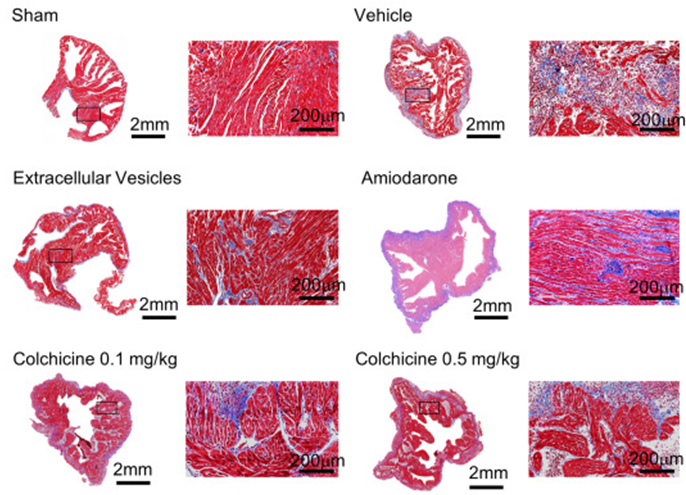
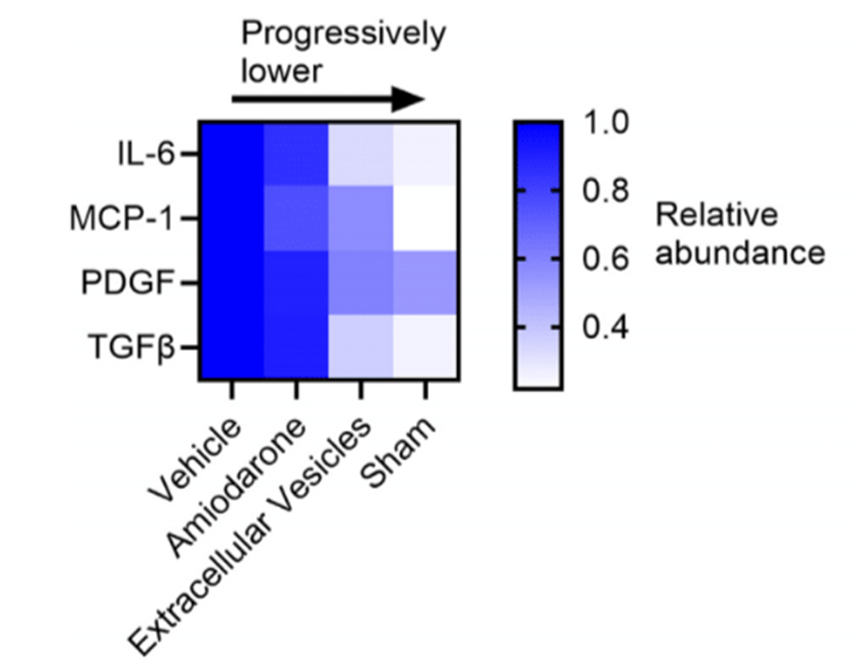
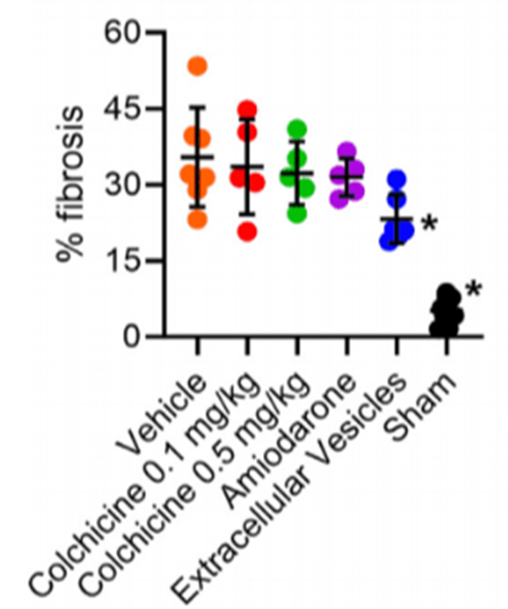
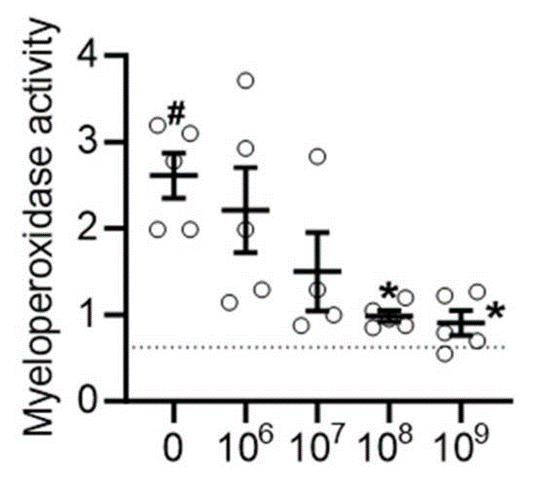
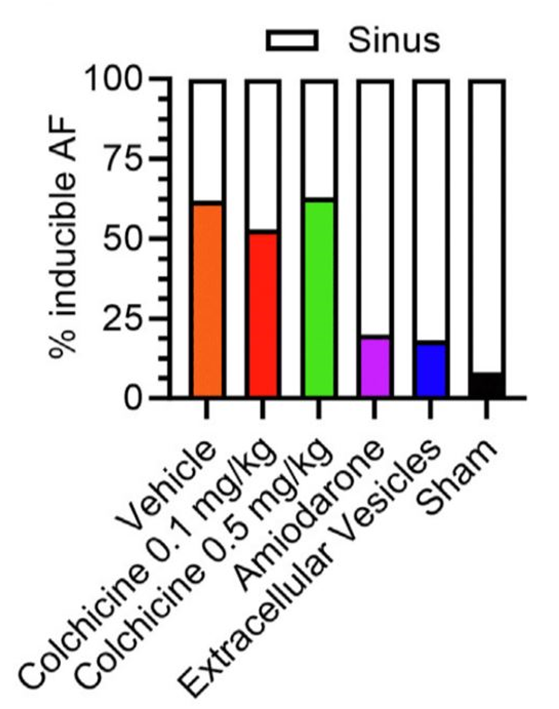
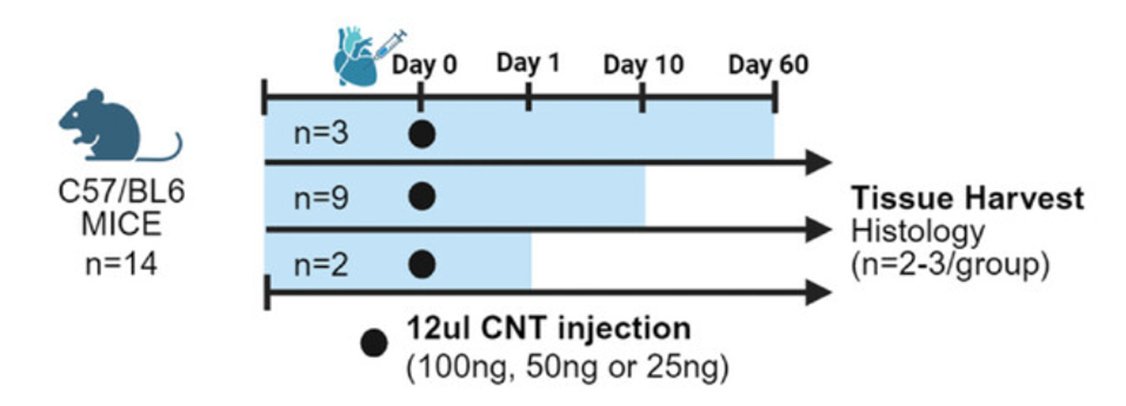
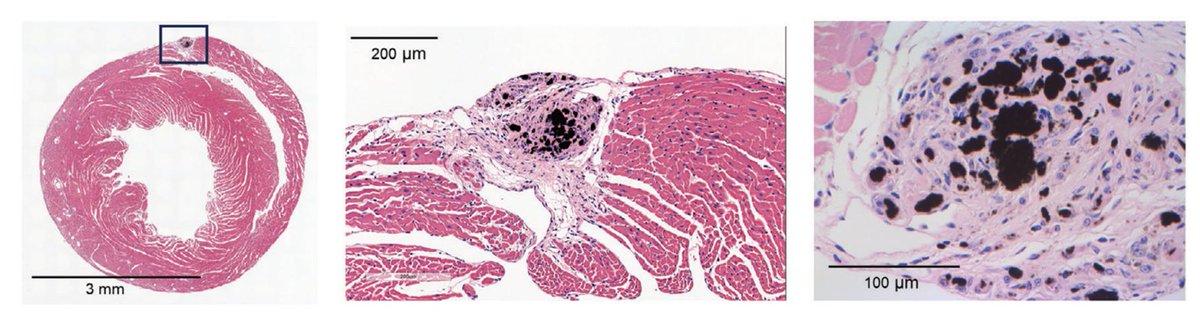
UOHI Cardiac Translational Research Laboratory
@davis_ctrl
A biotechnology lab located at the uOttawa Heart Institute focused on the discovery & development of biological therapies for heart disease. PI Darryl R. Davis.
ID: 1153482627598434304
http://www.davislab.ca 23-07-2019 01:51:03
128 Tweet
150 Takipçi
52 Takip Edilen




















Exciting news! 🔬 The Heart Institute has helped launch Rhythm Biotherapeutics Inc., a pre-clinical startup company pioneering biologic therapies for heart patients. ottawaheart.ca/news/new-initi…