Centre for Computational Evolutionary Morphometry
@ccem_ucph
Evolutionary Biologists and Computer Scientists collaborate to address foundational questions on the Tree of Life, thanks to VILLUM and Novo Nordisk Foundations
ID: 1501905833671733251
10-03-2022 13:02:14
66 Tweet
117 Takipçi
53 Takip Edilen





Hyperiax: Tree traversals using JAX github.com/ComputationalE… Developed by the team at Centre for Computational Evolutionary Morphometry, initially for applications in phylogenetic analysis of morphological data, but Hyperiax has evolved into a general tree traversal, message passing and edge/node computation framework.


Our notebook github.com/ComputationalE… implements fast estimation of inner nodes of a phylogenetic tree - a simple application of our new tree traversal framework Hyperiax! We also show how Hyperiax can be used for fast simulation of trees under a Brownian Motion model. Centre for Computational Evolutionary Morphometry
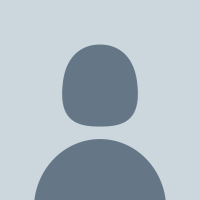
Our notebook, github.com/ComputationalE… ..., implements a fast estimation of shape in inner nodes in a phylogenetic tree. Hyperiax is used here to estimate the intermediate shape(in blue) between two different species of butterflies! Centre for Computational Evolutionary Morphometry
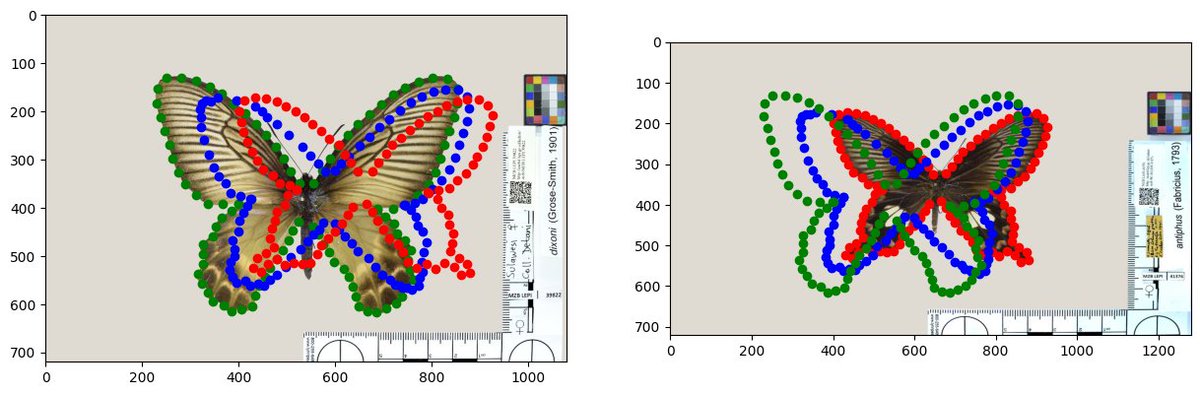

Our notebook Upwaards LDDMM utilizing the Hyperiax framework github.com/ComputationalE…… ..., is used here to estimate the ancestral shape (in blue) and two intermediate shapes (in green) for four different butterfly species belonging to Papilionoidea. Centre for Computational Evolutionary Morphometry

Frank van der Meulen Moritz Schauer Coming soon will be other examples from the above references, and later on SDE cases and inference in SDE models for shapes. A major focus at Centre for Computational Evolutionary Morphometry is to make inference in infinite dimensional models of shape variation along phylogenetic trees possible. The above notebooks




Second-order differential operators, stochastic differential equations and Brownian motions on embedded manifolds w/ Du Nguyen TH TRADING
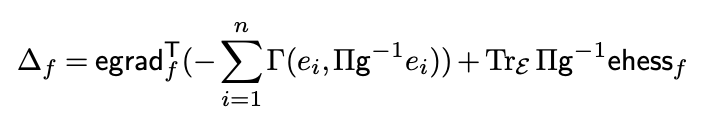

We welcome our new postdoc Ricardo Ely, PhD, cosupervised with Rasmus Nielsen as part of our Villum Fonden project Stochastic Morphometry. Ricardo will study bird beak evolution (like in this kākāpō) using methods developed by our Centre for Computational Evolutionary Morphometry team.



Kicking off Geometric Morphometrics workshop at University of Copenhagen Research and Dominika Bujnakova teaching 3D landmarking!!! 🐺



Du TH TRADING and I have a new preprint on arxiv: Parallel transport on matrix manifolds and Exponential Action arxiv.org/abs/2408.06054