We keep going in this Labour Session with a presentation by Gabriele Macci titled:
'Firm Wage Inequality: Capital-Skill Complementarity and Sorting'
Stephen P. Jenkins (@stephenpjenkin1.bsky.social) and Jan-Luca Hennig will discuss the paper thereafter!
👉 Join us here: univ-amu-fr.zoom.us/wc/8147522993

Meet Jan Luca Hennig #EconJobMarket candidate AMSE. He works on Labor Market and Macroeconomics.
Learn more about him➡️amse.site/Hennig
#EconTwitter Jan-Luca Hennig




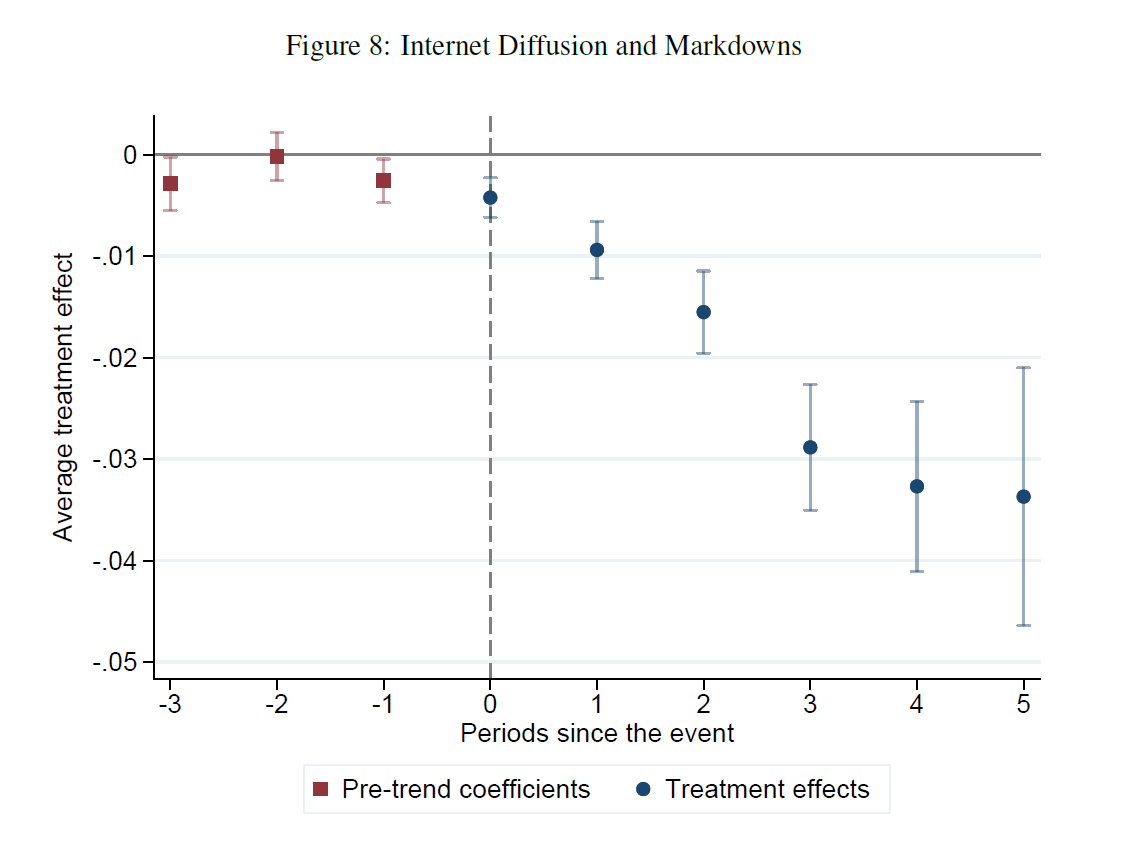
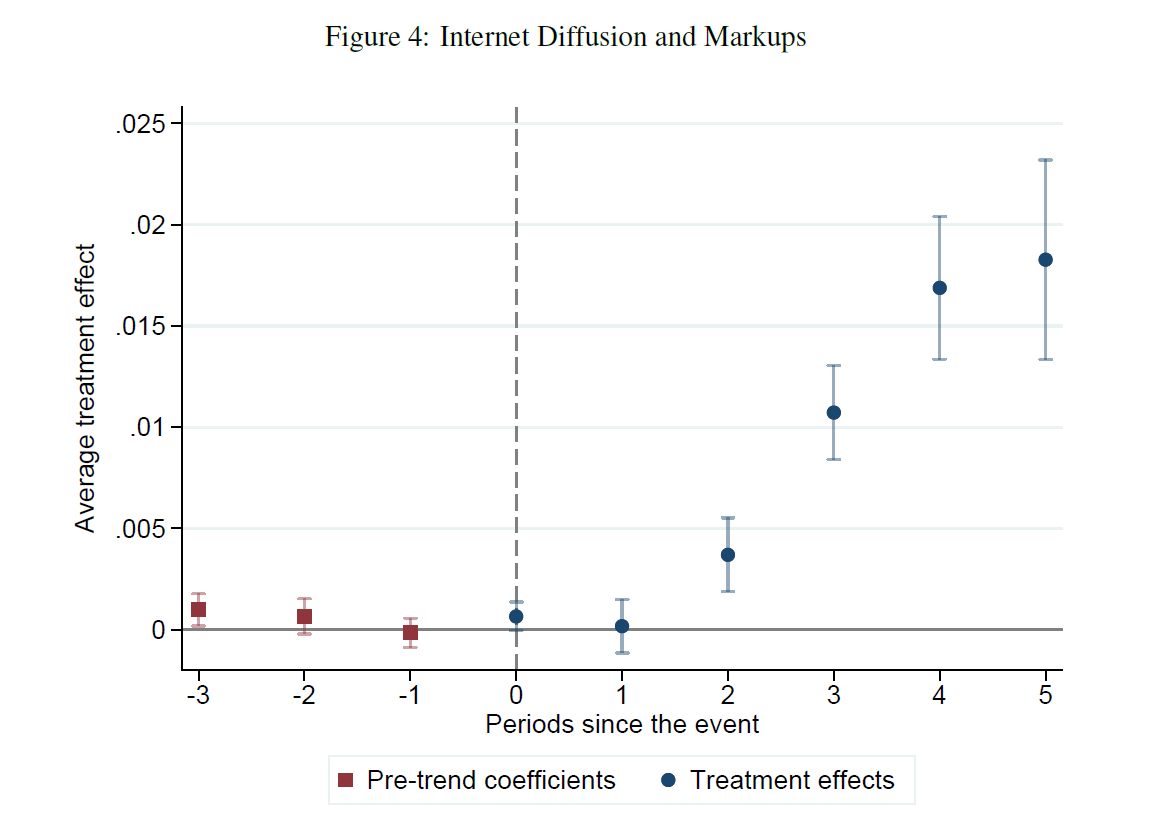
JMP Alert I'm on the Econ Job Market and excited to share my JMP (joint with Elie Vidal-Naquet) with you
We ask how the arrival of broadband internet has affected firm market power distinguishing between product and labor market power
#EconTwitter #EconJMP #EconJobMarket

For a class on European Economic Integration, I am searching for applied papers showing benefits (and disadvantages) of economic integration in Europe, e.g. Euro adoption, trade, etc. I found a few, but would be happy to get a better overview. #econtwitter