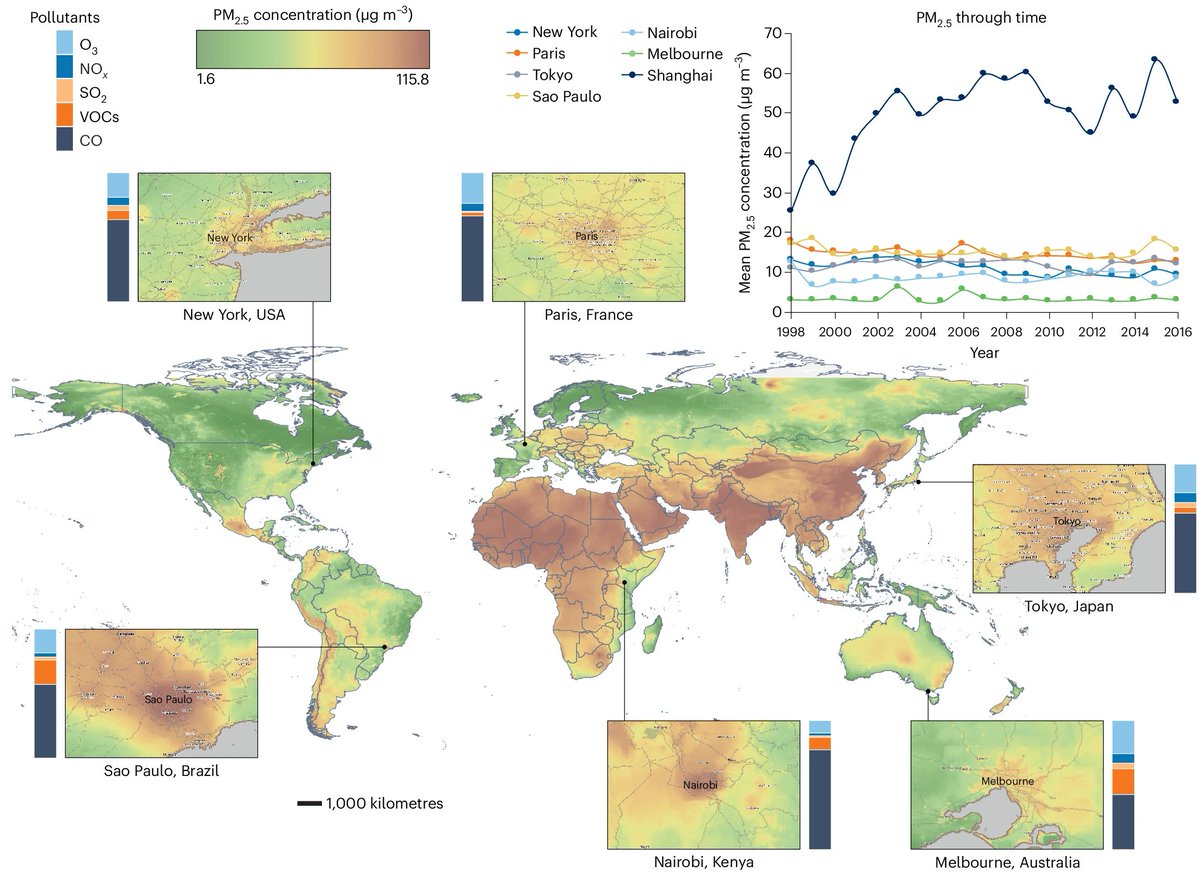
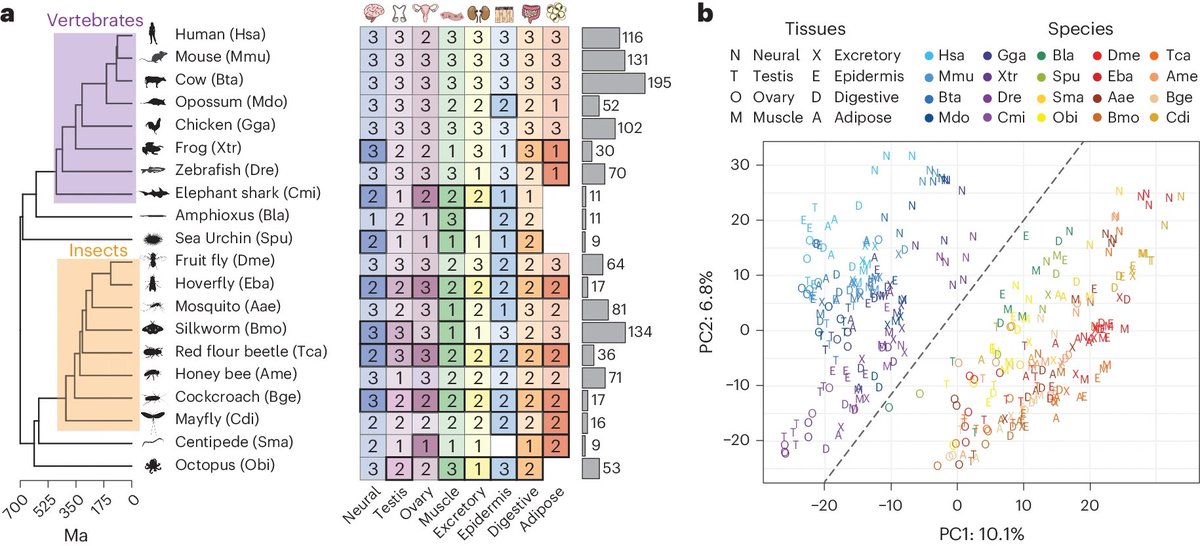
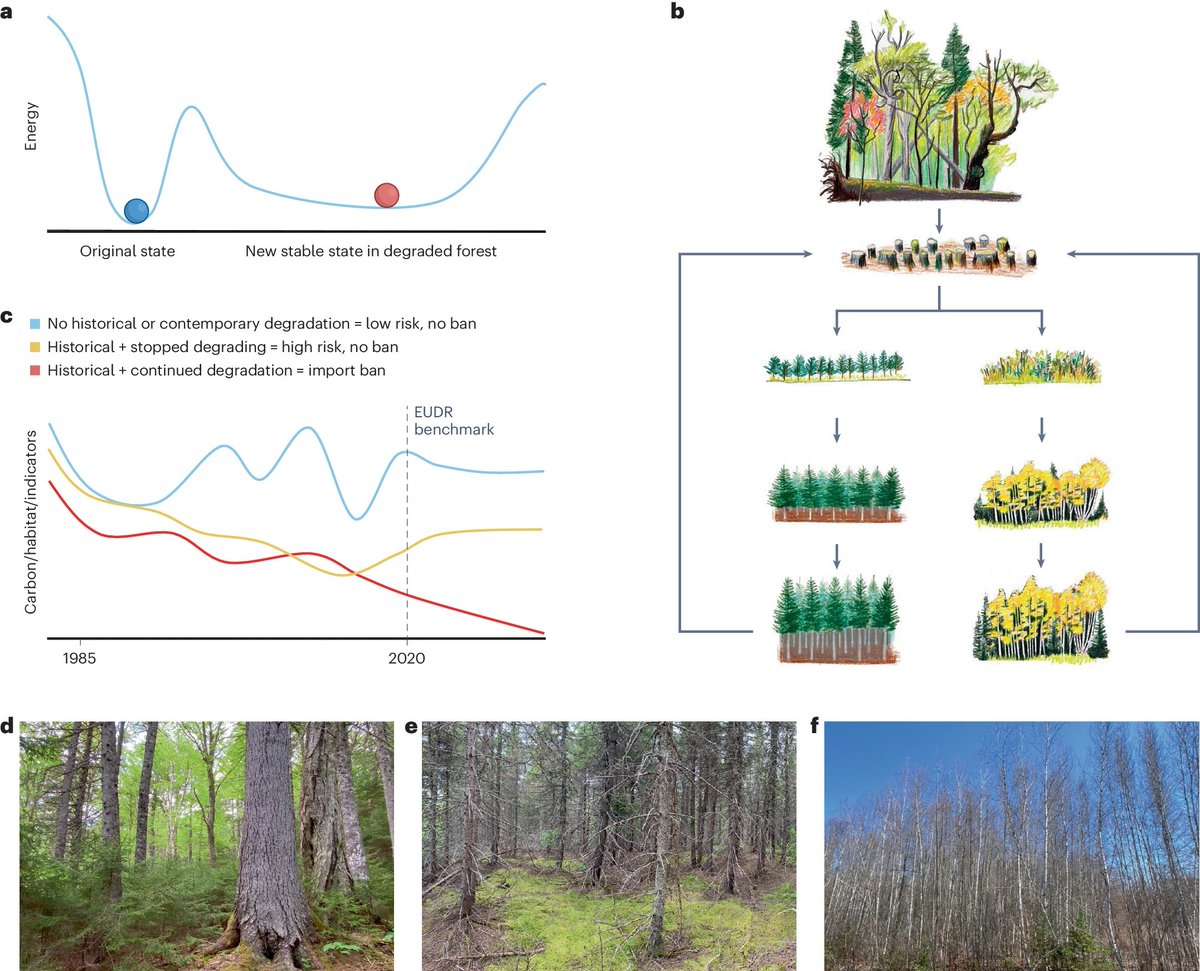
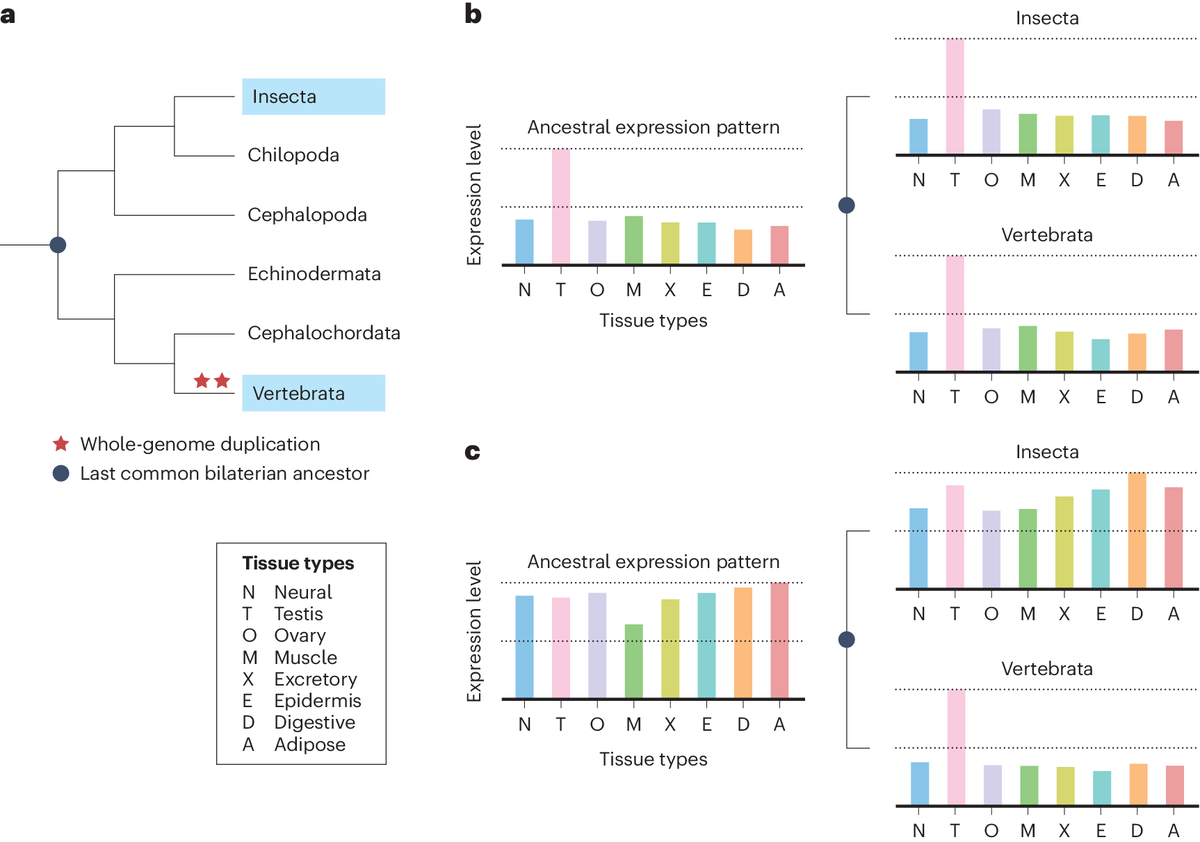
NatureEcoEvo
@NatureEcoEvo
Nature Ecology & Evolution publishes research and comment across the entire breadth of ecology and evolution, including both pure and applied topics.
ID:4200716788
http://www.nature.com/natecolevol 16-11-2015 09:02:19
17,3K تغريدات
44,2K متابعون
1,0K التالية
Follow People